RustFS Architecture
RustFS is an object storage system, similar to the well-known AWS S3. As a replacement for MinIO, RustFS references MinIO's simple, lightweight, scalable, and elegant architecture.
Objects can be documents, videos, PDF files, etc. To store objects, MinIO provides a scalable, flexible, and efficient solution for storing, accessing, and managing data. Its compatibility with AWS S3 API enables seamless integration with applications based on AWS S3.
The architecture diagram is as follows:
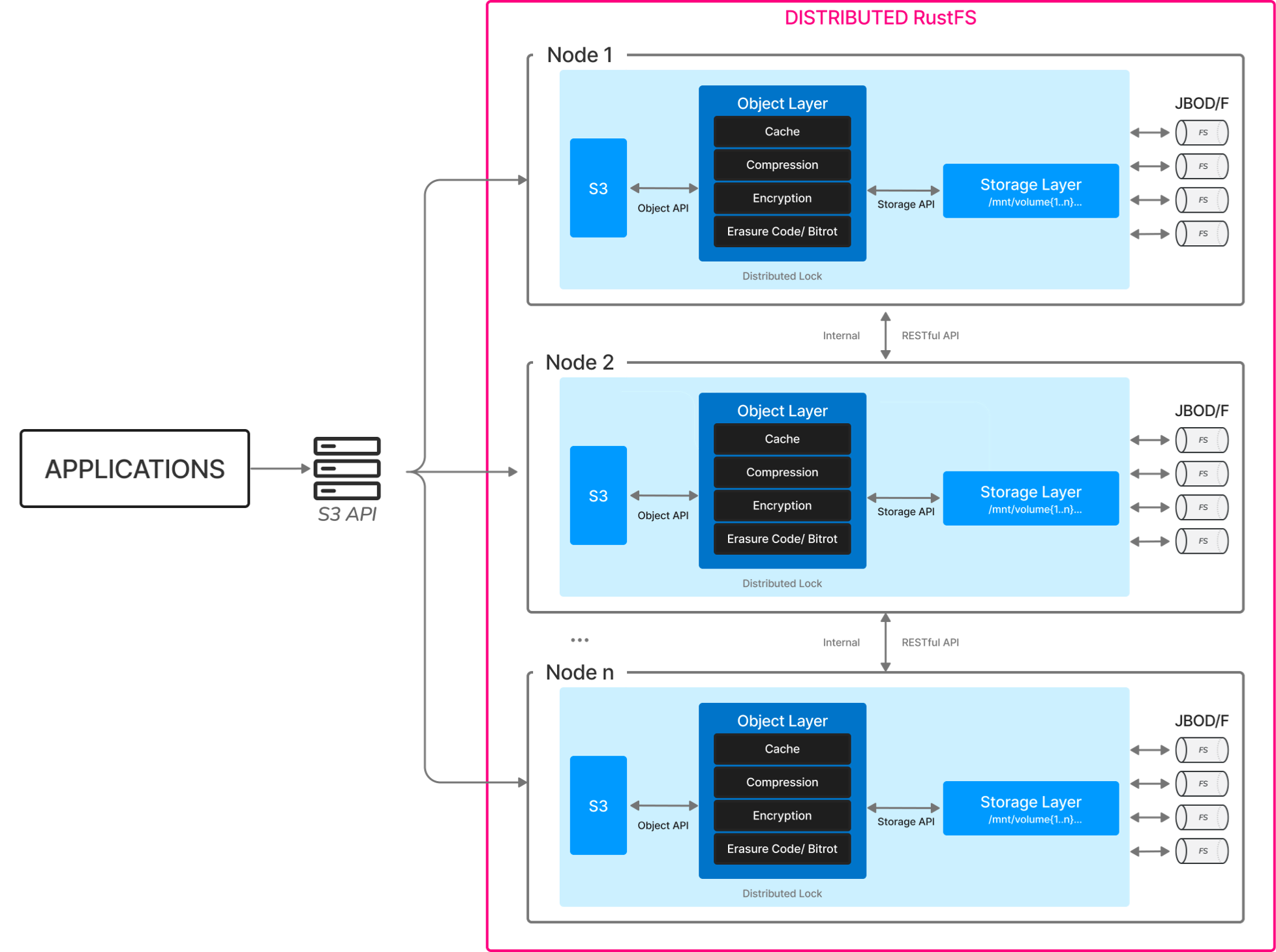
This is the basic architecture of RustFS. A distributed grid is a computer architecture that uses multiple nodes to perform a single task. Nodes are connected to each other through a network, which enables them to communicate with each other.
Consistency Design
In both distributed and single-machine modes, all read and write operations strictly follow the read-after-write consistency model.
Several Important Concepts in RustFS
Object: The basic object stored in Minio, such as files, byte streams, anything...
Bucket: A logical space used to store Objects. Data between each Bucket is mutually isolated. For clients, it is equivalent to a top-level folder for storing files.
Drive: The disk that stores data, passed as a parameter when MinIO starts. All object data in Minio will be stored in Drives.
Set: A collection of Drives. Distributed deployment automatically divides into one or more Sets based on cluster scale, with Drives in each Set distributed in different locations. An object is stored on one Set. (Some places also refer to the combination of Sets as Strips).
Therefore, when designing architecture and deploying equipment, it should be noted that:
An object is stored on one Set;
A cluster is divided into multiple Sets;
The number of Drives contained in a Set is fixed, automatically calculated by the system based on cluster scale by default;
Drives in a Set are distributed across different nodes as much as possible;
Special Thanks
Traditional distributed storage architectures must have: Master nodes, MetaData nodes, and Data Node nodes. This design makes user deployment very complex. At the same time, without rich distributed storage management experience, once metadata is lost, there is a risk of data loss.
All nodes are at the same hierarchical level, greatly simplifying architectural design and eliminating concerns about metadata loss, allowing startup with a single command.
Without losing elegance, simplicity, and reliability, RustFS adopts the same architectural design as MinIO.
Thanks to MinIO for proposing this architectural concept, which has greatly facilitated users worldwide and promoted the S3 protocol.