Bare Metal Deployment
When deploying RustFS on bare metal servers, you can maximize hardware performance and achieve the best storage efficiency. This guide covers bare metal deployment best practices.
Hardware Requirements
Minimum Configuration
- CPU: 4 cores, 2.4GHz or higher
- Memory: 8GB RAM minimum, 16GB recommended
- Storage: At least 4 drives for erasure coding
- Network: Gigabit Ethernet
Recommended Configuration
- CPU: 16+ cores, 3.0GHz or higher
- Memory: 32GB+ RAM
- Storage: 8+ drives, mixed SSD/HDD for tiering
- Network: 10Gb Ethernet or higher
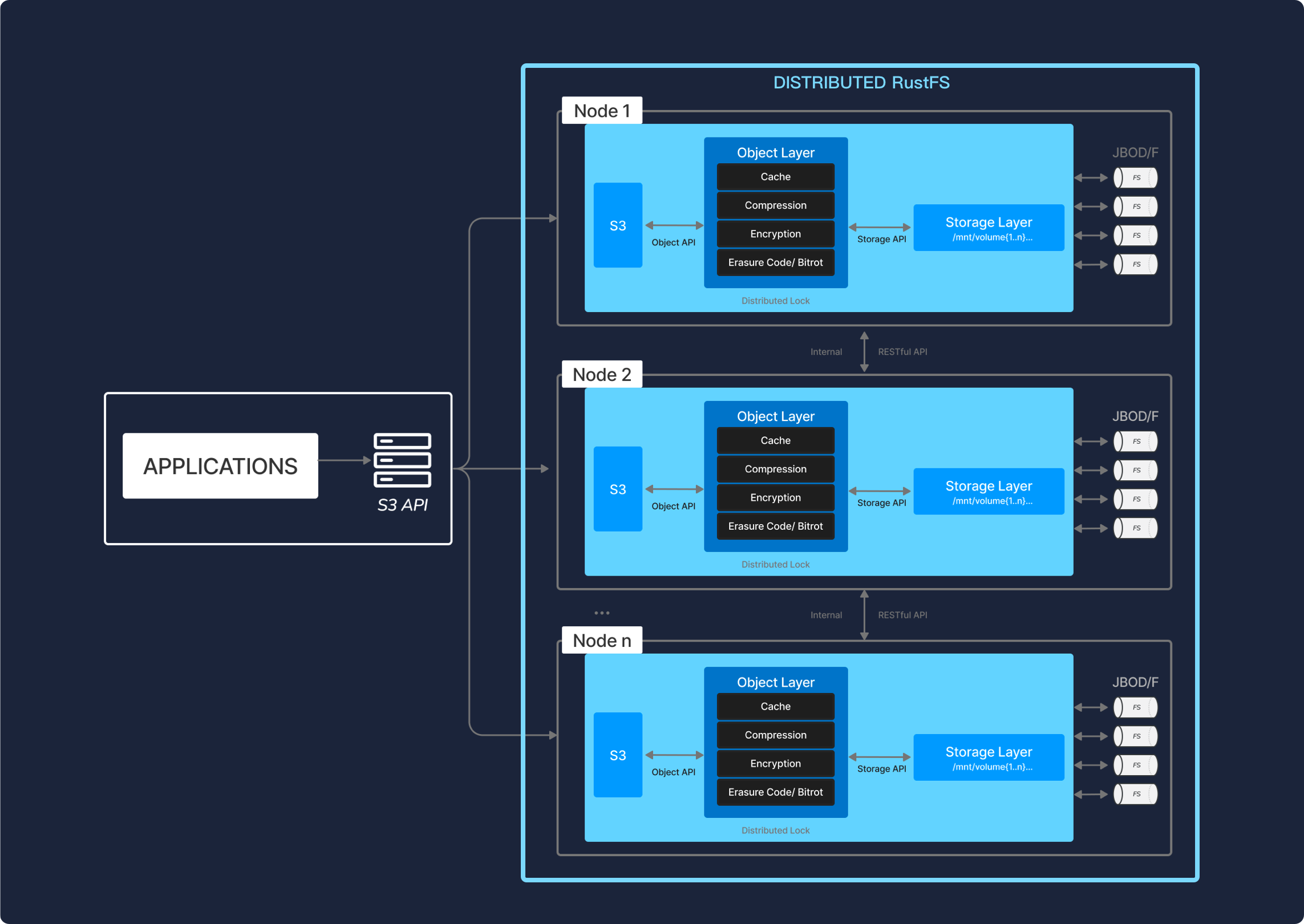
Deployment Architecture
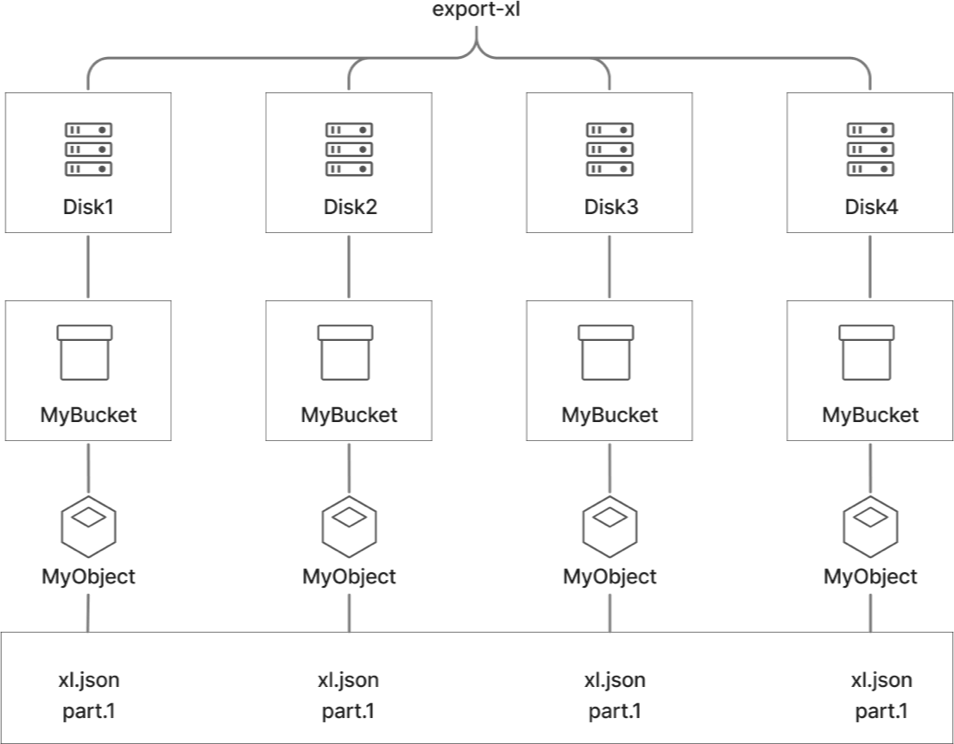
Single Node Mode (SNSD)
Suitable for development and testing environments:
bash
# Single node with single drive
rustfs server /data --console-address ":9001"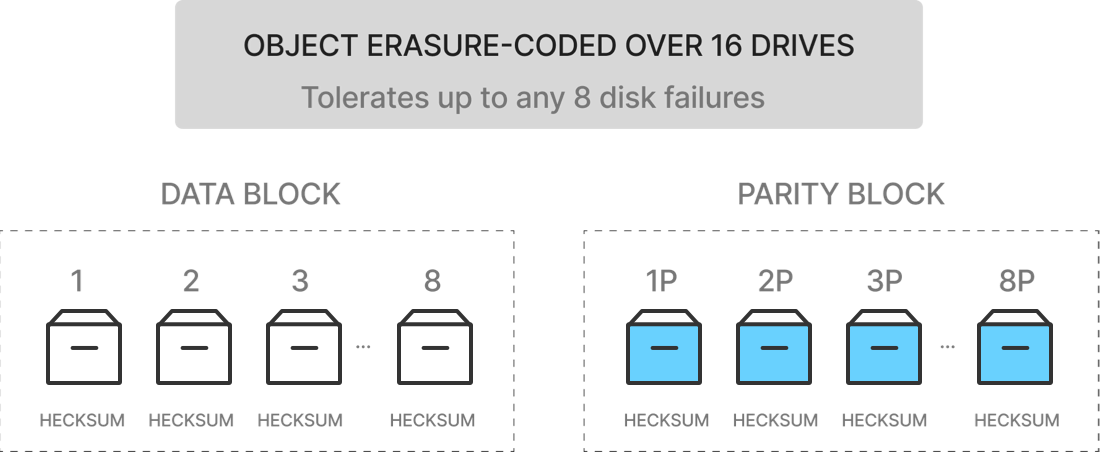
Multi-Node Mode (MNMD)
Recommended for production environments:
bash
# Node 1
rustfs server http://server{1...4}/data{1...4} \
--console-address ":9001"
# Node 2-4 (similar configuration)
Performance Optimization
Storage Configuration
Drive Selection
- Use enterprise-grade drives for production
- Consider NVMe SSDs for high-performance workloads
- Separate OS and data drives
RAID Configuration
- Disable hardware RAID for object storage
- Use JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks) mode
- Let RustFS handle redundancy
Network Optimization
Network Bonding
bash# Configure network bonding for redundancy sudo modprobe bonding echo "balance-rr" > /sys/class/net/bond0/bonding/modeJumbo Frames
bash# Enable jumbo frames for better throughput sudo ip link set dev eth0 mtu 9000
Monitoring and Maintenance
Health Monitoring
- Monitor drive health with SMART tools
- Track network utilization and latency
- Set up alerts for hardware failures
Maintenance Procedures
Drive Replacement
- Hot-swap failed drives
- Monitor healing process
- Verify data integrity
Node Maintenance
- Graceful node shutdown
- Rolling updates
- Capacity planning
Security Considerations
Physical Security
- Secure server room access
- Environmental monitoring
- Power redundancy
Network Security
- Firewall configuration
- Network segmentation
- TLS encryption for client connections
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Drive Failures
- Check SMART status
- Replace failed drives promptly
- Monitor healing progress
Network Issues
- Verify network connectivity
- Check bandwidth utilization
- Monitor for packet loss
Performance Issues
- Analyze I/O patterns
- Check for CPU/memory bottlenecks
- Optimize drive layout