Distributed Deployment
RustFS provides enterprise-grade distributed object storage capabilities, supporting multi-node clusters for high availability and scalability.
Architecture Overview
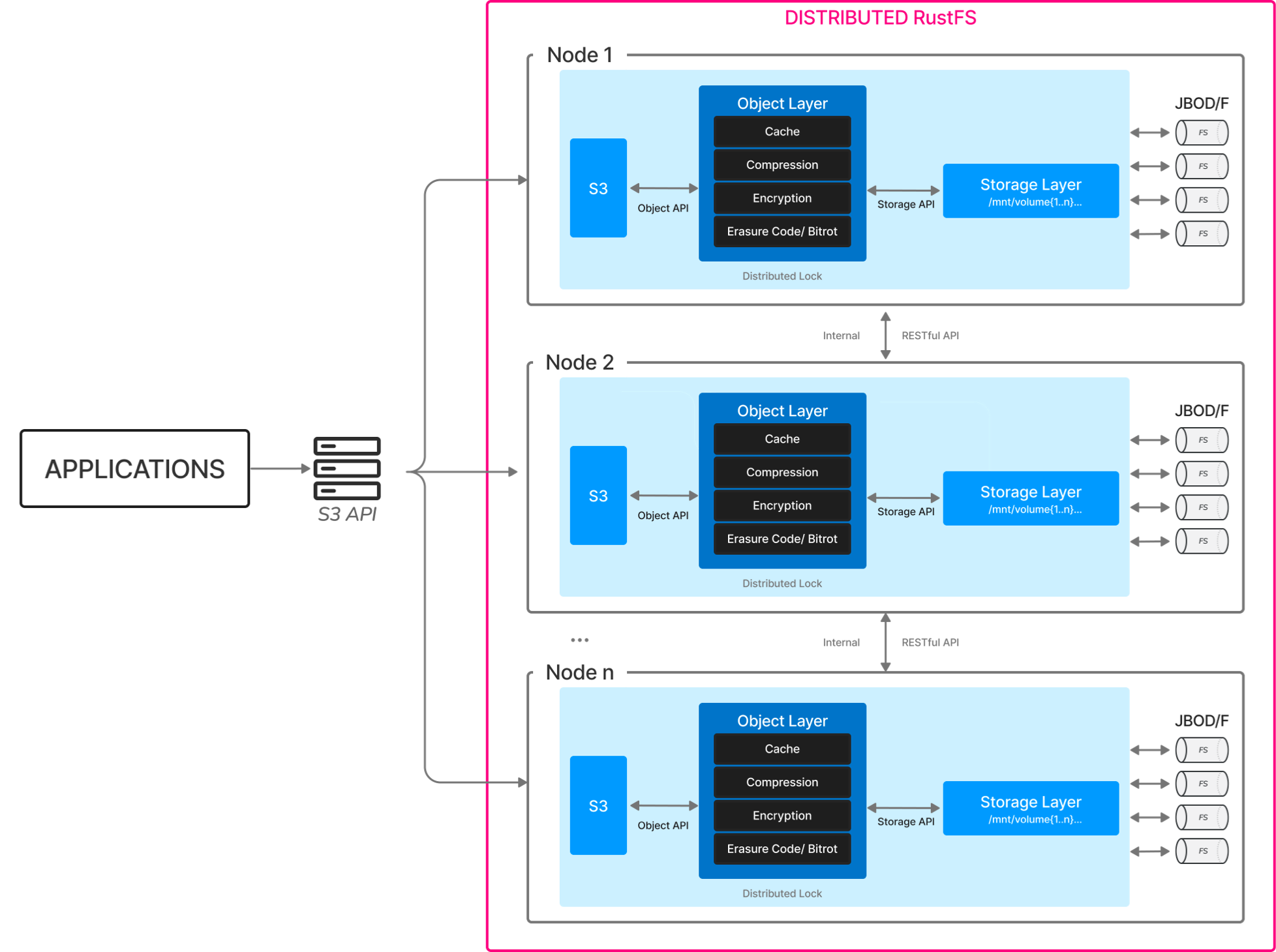
RustFS uses a distributed architecture without single points of failure. Each node in the cluster can serve both read and write requests, providing:
- High Availability: Automatic failover and recovery
- Linear Scalability: Add nodes to increase capacity and performance
- Data Durability: Configurable erasure coding for data protection
- Load Distribution: Automatic load balancing across nodes
Deployment Modes
Multi-Node Multi-Drive (MNMD)
The recommended production deployment mode:
bash
# 4 nodes, 4 drives each (16 drives total)
rustfs server http://node{1...4}.example.com/data{1...4} \
--console-address ":9001"Benefits:
- Maximum fault tolerance
- Best performance scaling
- Optimal for large-scale deployments
Multi-Node Single-Drive (MNSD)
Suitable for environments with external storage:
bash
# 4 nodes, 1 drive each
rustfs server http://node{1...4}.example.com/data \
--console-address ":9001"Use Cases:
- Cloud deployments with attached storage
- Containerized environments
- Testing and development
Cluster Configuration
Node Requirements
Minimum Configuration:
- 4 nodes for basic redundancy
- 8GB RAM per node
- Gigabit network connectivity
Recommended Configuration:
- 8+ nodes for production
- 16GB+ RAM per node
- 10Gb network connectivity
Erasure Coding
RustFS automatically selects optimal erasure coding based on cluster size:
| Nodes | EC Configuration | Fault Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | EC:2+2 | 2 node failures |
| 8 | EC:4+4 | 4 node failures |
| 12 | EC:6+6 | 6 node failures |
| 16+ | EC:8+8 | 8 node failures |
High Availability Features
Automatic Failover
- Immediate detection of node failures
- Automatic request routing to healthy nodes
- No manual intervention required
Data Healing
- Continuous background healing process
- Automatic reconstruction of lost data
- Proactive replacement of degraded objects
Rolling Updates
- Zero-downtime software updates
- Gradual node updates with health checks
- Automatic rollback on failure
Performance Optimization
Network Optimization
Dedicated Network
bash# Use dedicated network interfaces for cluster traffic rustfs server http://node{1...4}.internal:9000/data{1...4}Load Balancing
- Deploy load balancer in front of cluster
- Use health checks for automatic failover
- Distribute client connections evenly
Storage Optimization
Drive Selection
- Use consistent drive types across nodes
- Consider NVMe for high-performance workloads
- Plan for drive replacement cycles
Capacity Planning
- Monitor storage utilization trends
- Plan expansion before reaching 80% capacity
- Consider seasonal usage patterns
Monitoring and Alerting
Key Metrics
- Node Health: CPU, memory, disk usage
- Network: Bandwidth, latency, packet loss
- Storage: Capacity, IOPS, healing status
- Cluster: Object count, data distribution
Alert Configuration
bash
# Example Prometheus alerts
- alert: NodeDown
expr: up{job="rustfs"} == 0
for: 1m
- alert: HighDiskUsage
expr: disk_usage_percent > 80
for: 5mDisaster Recovery
Multi-Site Deployment
- Deploy clusters across multiple data centers
- Configure cross-site replication
- Implement disaster recovery procedures
Backup Strategies
- Regular data exports to external storage
- Point-in-time recovery capabilities
- Automated backup verification
Security
Cluster Security
- TLS encryption for inter-node communication
- Certificate-based node authentication
- Network segmentation for cluster traffic
Access Control
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Integration with external identity providers
- Audit logging for all operations
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Split-Brain Prevention
- Ensure odd number of nodes when possible
- Configure proper quorum settings
- Monitor network connectivity
Performance Degradation
- Check for failing drives
- Monitor network utilization
- Analyze access patterns
Capacity Issues
- Monitor storage growth trends
- Plan expansion proactively
- Implement lifecycle policies