Bucket and Object Versioning
RustFS Object Storage Provides AWS S3 Versioning Compatibility
Object-level versioning is a significant improvement compared to SAN and NAS versioning methods. Versioning not only provides data protection but also serves as the foundation for powerful features such as object locking, immutability, tiering, and lifecycle management.
With RustFS, objects are versioned independently according to Amazon's S3 structure/implementation. RustFS assigns a unique ID to each version of a given object - applications can specify a version ID at any time to access a point-in-time snapshot of that object.
Versioning allows users to preserve multiple variants of an object in the same bucket and provides a mechanism to save, retrieve, and restore every version of every object stored in the bucket, eliminating the need for snapshots. Versioning ensures objects remain available through a series of failures, including those caused by application and human errors.
Versioning is enabled at the bucket level. Once enabled, RustFS automatically creates a unique version ID for objects. The same object can have multiple versions.
One of the main benefits of versioning is preventing accidental overwrites or deletions. This is implemented using the concept of delete markers. When a versioned object is deleted, it is not permanently removed. Instead, a delete marker is created and becomes the current version of the object. When that object is requested, RustFS returns a 404 Not Found message. The object can be restored by deleting the delete marker.
Similarly, if a versioned object is overwritten, RustFS creates a new version and it becomes the current version. Likewise, old versions can be restored as needed.
RustFS Supports Object Versioning with Three Different Bucket States

Note that once versioning is enabled for a bucket, the operation cannot be undone - it can only be suspended. Versioning is a global setting in the bucket - meaning all objects are now versioned.
Users with appropriate permissions can suspend versioning to stop accumulating object versions. Similar to enabling versioning, this operation is performed at the bucket level.
Like all RustFS features, versioning can be applied using the RustFS console, client (mc), SDK, or through command-line applications.
Versioning is the simplest way to protect data from accidental operations. However, as objects are versioned, it leads to larger bucket sizes and may result in more interdependencies between objects and risks of hidden object dependencies. These factors can be mitigated through lifecycle management.
Core Feature Advantages
In addition to its data protection benefits, RustFS's object storage versioning serves as the foundation for other key features
Main Feature Characteristics
- ✅ Bucket Replication (Active-Active, Active-Passive)
- ✅ Mc undo - Rollback PUT/DELETE objects with a single command
- ✅ Object Lock
- ✅ Continuous Data Protection-like protection without the overhead of snapshots or full system replication
- ✅ Mc rewind - View buckets or objects at any point in time after versioning is enabled
Architecture
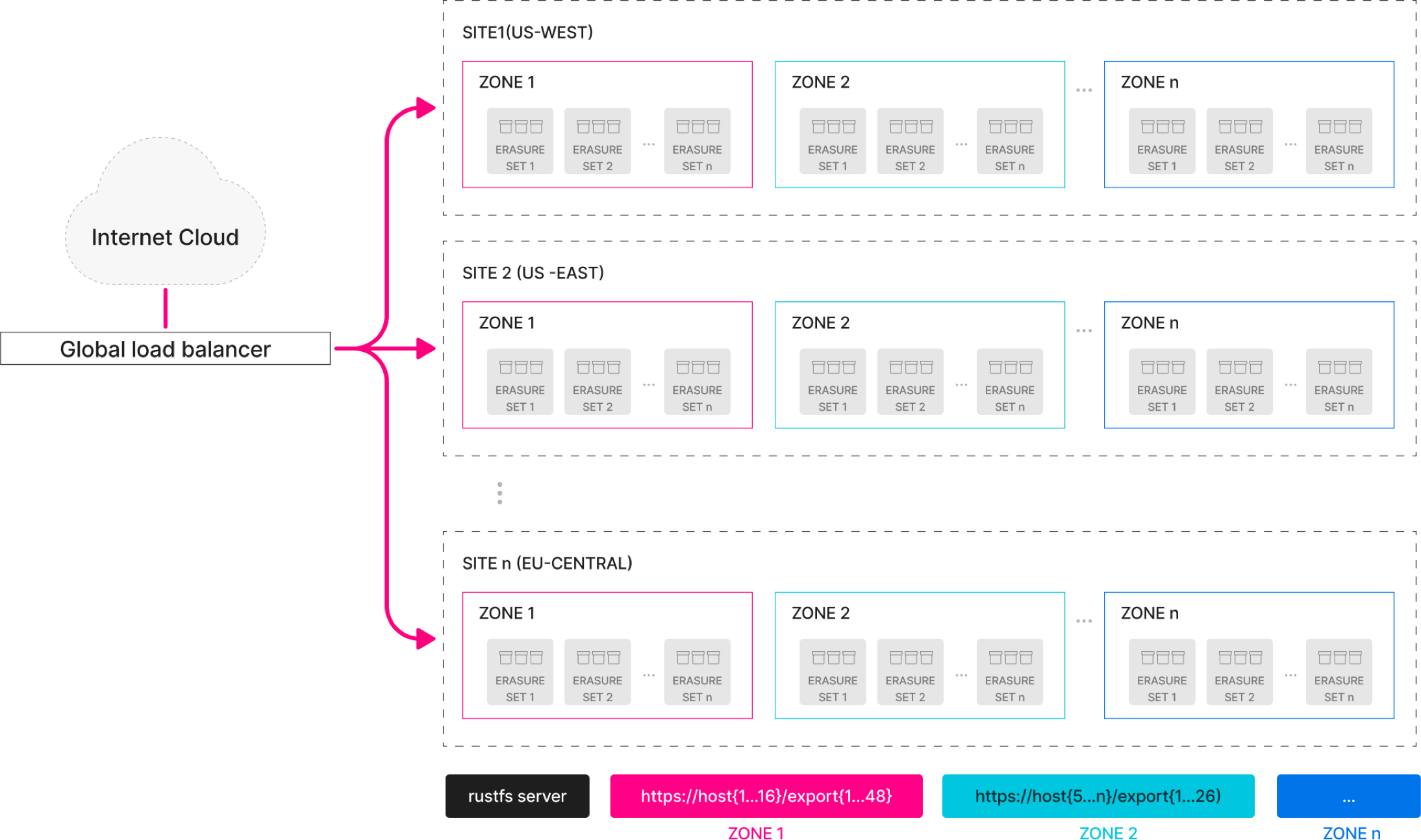
System Requirements
Versioning requires: Erasure coding and at least four disks.
Versioning States
RustFS supports three different bucket versioning states:
- 🔴 Unversioned - Default state, no versioning performed
- 🟢 Enabled - Full versioning functionality, assigns unique ID to each object version
- 🟡 Suspended - Stops accumulating new versions but retains existing versions
Key Features
- 🆔 Unique Version ID - Each object version has a unique identifier
- 🔄 Point-in-Time Recovery - Can access any historical version of an object
- 🛡️ Delete Protection - Uses delete markers to prevent accidental deletion
- 📊 Lifecycle Management - Automatically manages version count and storage costs
- 🔐 Permission Control - Fine-grained access permission management