RustFS for Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
Three Reasons Customers Run RustFS on Amazon EKS
- RustFS serves as a consistent storage layer in hybrid cloud or multi-cloud deployment scenarios
- RustFS is a Kubernetes-native high-performance product that can provide predictable performance in public cloud, private cloud, and edge cloud environments.
- Running RustFS on OpenShift provides flexible control over the software stack, avoiding cloud lock-in.
Red Hat® OpenShift® is an enterprise-grade Kubernetes container platform with full-stack automated operations capabilities that can manage hybrid cloud, multi-cloud, and edge deployments. OpenShift includes enterprise-grade Linux operating systems, container runtimes, networking, monitoring, registries, and authentication and authorization solutions.
RustFS natively integrates with OpenShift, making it easier to operate your own large-scale multi-tenant object storage as a service. RustFS Operator works with OpenShift toolchain (such as OpenShift Cluster Manager CLI and Quay container registry) to ensure you get maximum return on investment from the OpenShift ecosystem.
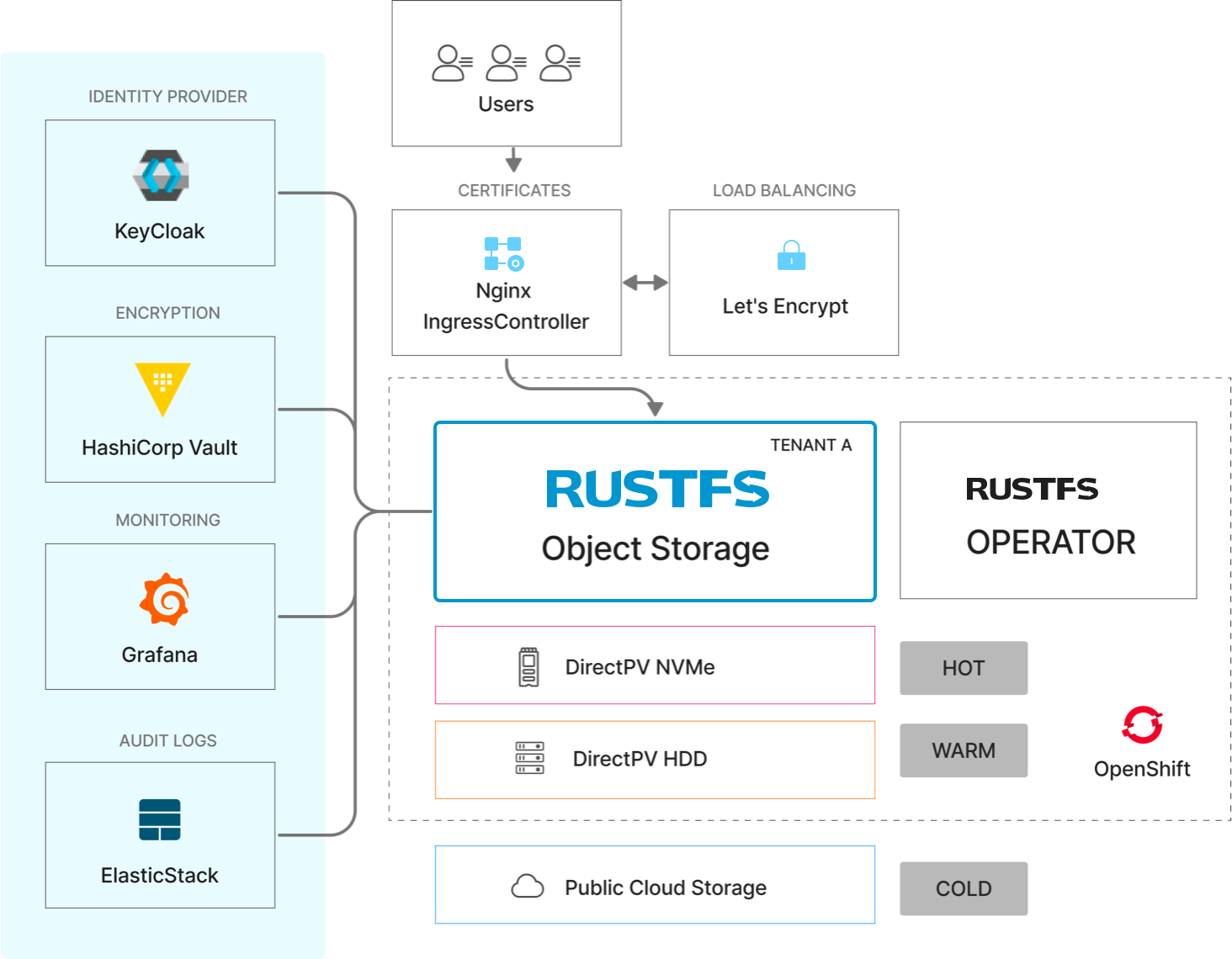
RustFS provides consistent, high-performance, and scalable object storage because it is Kubernetes-native by design and S3-compatible from the start. Developers can easily obtain Amazon S3-compatible persistent storage services for all cloud-native applications running on OpenShift. Unlike AWS S3, RustFS enables applications to scale across any multi-cloud and hybrid cloud infrastructure while still being manageable within the OpenShift ecosystem without public cloud lock-in.
RustFS Operator Natively Integrates with OpenShift Features
Feature Overview
- Storage Classes and Tiering
- External Load Balancing
- Encryption Key Management
- Identity Management
- Certificate Management
- Monitoring and Alerting
- Logging and Auditing
Storage Classes and Tiering
A key requirement for deploying RustFS at scale on Tencent Cloud TKE is capability tiers across storage classes (NVMe, HDD, public cloud). This enables enterprises to manage both cost and performance simultaneously.
RustFS supports automatic transition of aging objects from fast NVMe tiers to more cost-effective HDD tiers, and even to cost-optimized cold public cloud storage tiers.
When tiering, RustFS provides a unified namespace across tiers. Movement across tiers is transparent to applications and triggered by customer-determined policies.
RustFS provides secure storage in OpenShift hybrid clouds by encrypting objects at the source, ensuring customers always have complete control over data. When OpenShift is deployed in public clouds, tiering capabilities help OpenShift effectively manage data across persistent block storage and cheaper object storage tiers.
Learn More:
External Load Balancing
All RustFS communication is based on HTTP, RESTful APIs, and will support any standard Kubernetes-compatible ingress controller. This includes hardware and software-defined solutions. The most popular choice is NGINX. Install using OperatorHub or OpenShift Marketplace, then expose RustFS tenants using annotations.
Encryption Key Management
There are no native OpenShift key management capabilities. Therefore, RustFS recommends using HashiCorp Vault to store keys outside the object storage system. This is a best practice for cloud-native applications.
For all production environments, we recommend enabling encryption on all buckets by default. RustFS uses AES-256-GCM or ChaCha20-Poly1305 encryption to protect data integrity and confidentiality with negligible performance impact.
RustFS supports all three server-side encryption (SSE-KMS, SSE-S3, and SSE-C) modes. SSE-S3 and SSE-KMS integrate with server-side KMS, while SSE-C uses client-provided keys.
RustFS will use this KMS to bootstrap its internal key encryption server (KES service) for high-performance per-object encryption. Each tenant runs its own KES server in an isolated namespace.
Identity Management
When running RustFS on OpenShift, customers can manage single sign-on (SSO) through third-party OpenID Connect/LDAP compatible identity providers (such as Keycloak, Okta/Auth0, Google, Facebook, ActiveDirectory, and OpenLDAP). RustFS recommends OpenID Connect compatible Keycloak IDP.
External IDPs allow administrators to centrally manage user/application identities. RustFS builds on top of IDPs to provide AWS IAM-style user, group, role, policy, and token service APIs. The ability to have a unified identity and access management (IAM) layer independent of infrastructure provides significant architectural flexibility.
Certificate Management
All traffic from applications to RustFS, including inter-node traffic, is encrypted using TLS. TLS certificates are used to secure network communications and establish the identity of network connection resources, such as RustFS server domains.
RustFS integrates with OpenShift certificate manager, so you can use the RustFS operator to automatically provision, configure, manage, and update certificates for RustFS tenants. Tenants are completely isolated from each other in their own Kubernetes namespaces with their own certificates for enhanced security.
Monitoring and Alerting
RustFS recommends using Grafana, platform monitoring components installed in the OpenShift-user-workload-monitoring project, or any other OpenShift container monitoring tools to connect to RustFS. RustFS publishes all imaginable storage-related Prometheus metrics, from bucket capacity to access metrics. These metrics can be collected and visualized in any Prometheus-compatible tool or RustFS console.
External monitoring solutions periodically scrape RustFS Prometheus endpoints. RustFS recommends using Grafana or platform monitoring components installed in the openshift-user-workload-monitoring project to connect to RustFS. These same tools can also be used to establish baselines and set notification alert thresholds, which can then be routed to notification platforms like PagerDuty, Freshservice, or even SNMP.
Logging and Auditing
Enabling RustFS auditing generates logs for every operation on the object storage cluster. In addition to audit logs, RustFS also logs console errors for operational troubleshooting.
RustFS supports outputting logs to Elastic Stack (or third-party) for analysis and alerting.